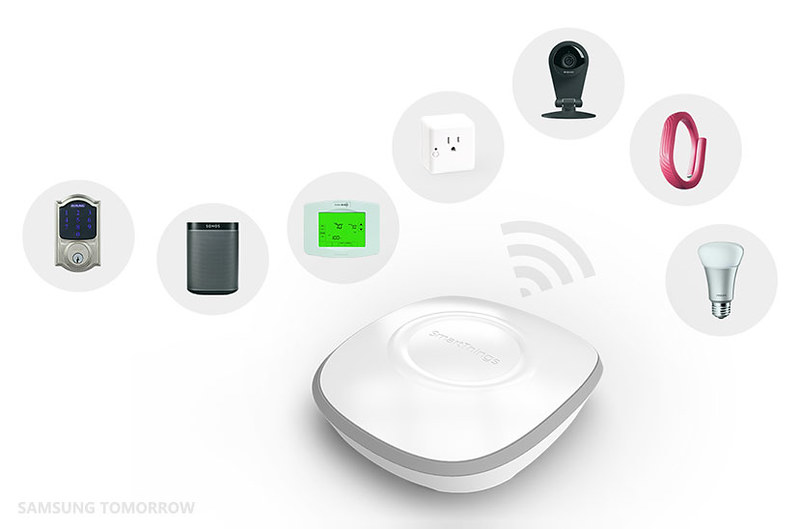
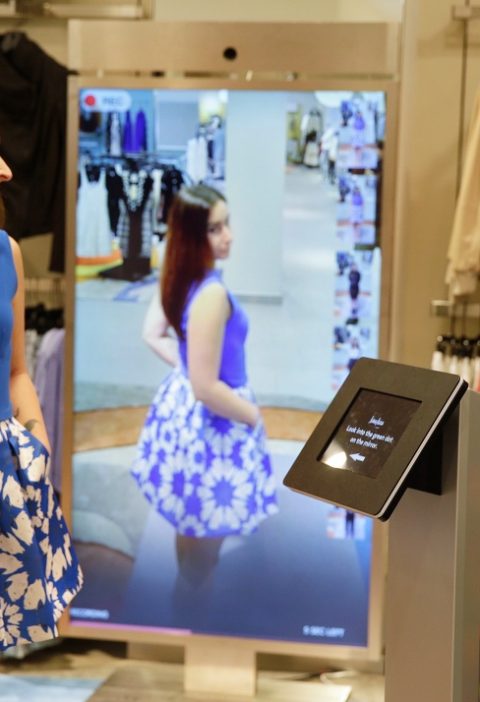
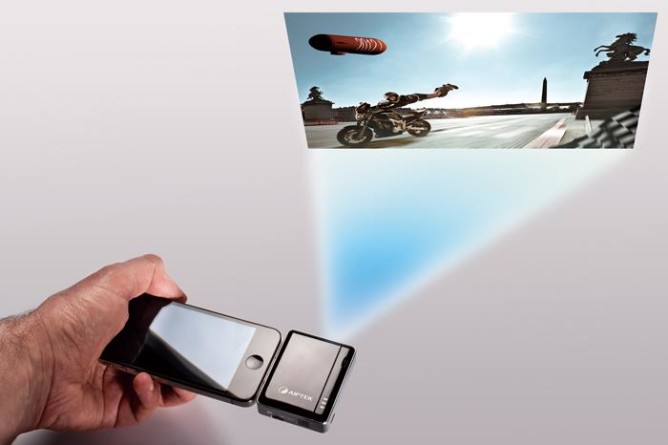
Hidden Gems of the Gadget World: Unearthing Obscure but Remarkable Tech
In a world saturated with gadgets and technological innovations, it’s easy to become enamored by the latest and greatest devices that dominate the market. But there’s an enchanting realm of lesser-known gadgets, often overshadowed by their more popular counterparts. These hidden gems of the gadget world are often obscure but hold the potential to enhance …