Controllers and Thermostats for Electric Heating
Contents
– Thermostats integrated with radiators: the most basic
– Electronic thermostats: for more autonomy!
– Centralized electric heating controllers: the most efficient
– Outdoor sensor: take into account climatic variations
– Load shedding switch: to avoid overcharging
Several types of electric heating controllers (from a simple thermostat to a centralized system) allow you to regulate the temperature of your electric radiators. This way, you will improve your comfort and will be able to reduce your hydro bill.
Thermostats integrated into radiators: the most basic.
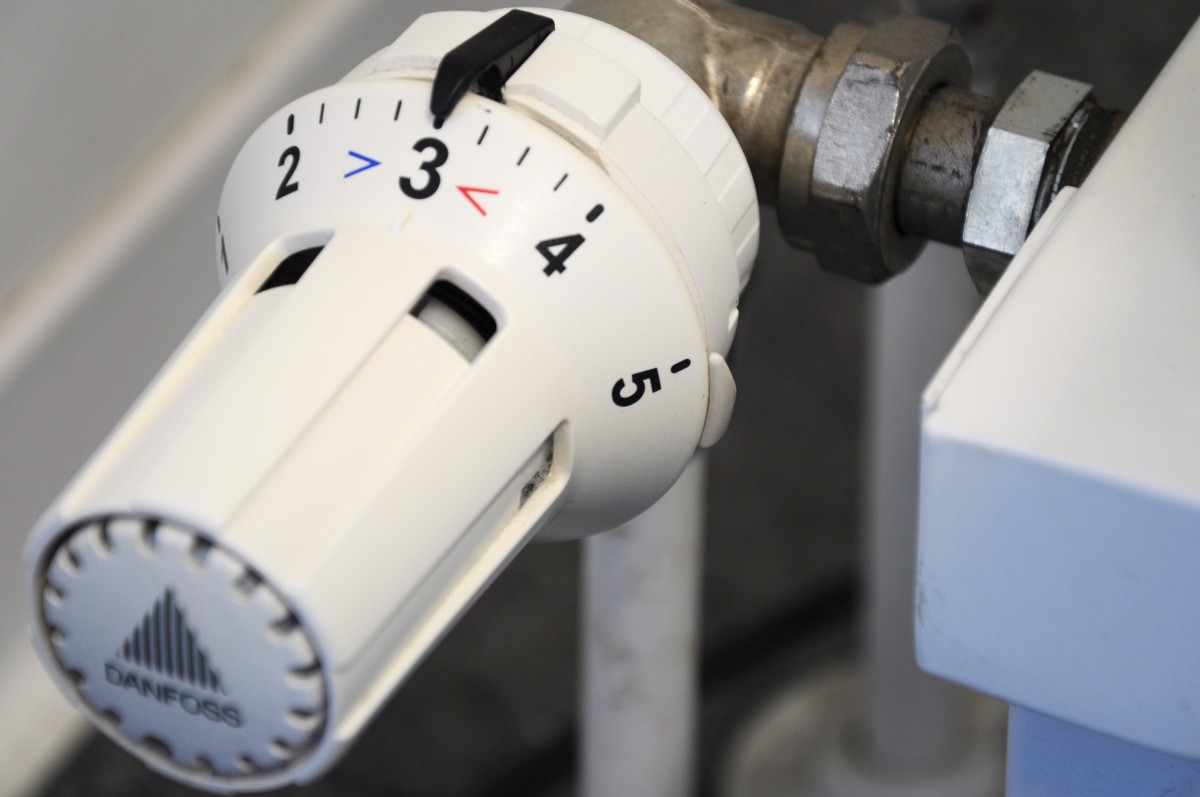
The electric radiator thermostat is fitted to all radiators, even the oldest. On low-end or old radiators, these thermostats act on the heating power: level 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, off.
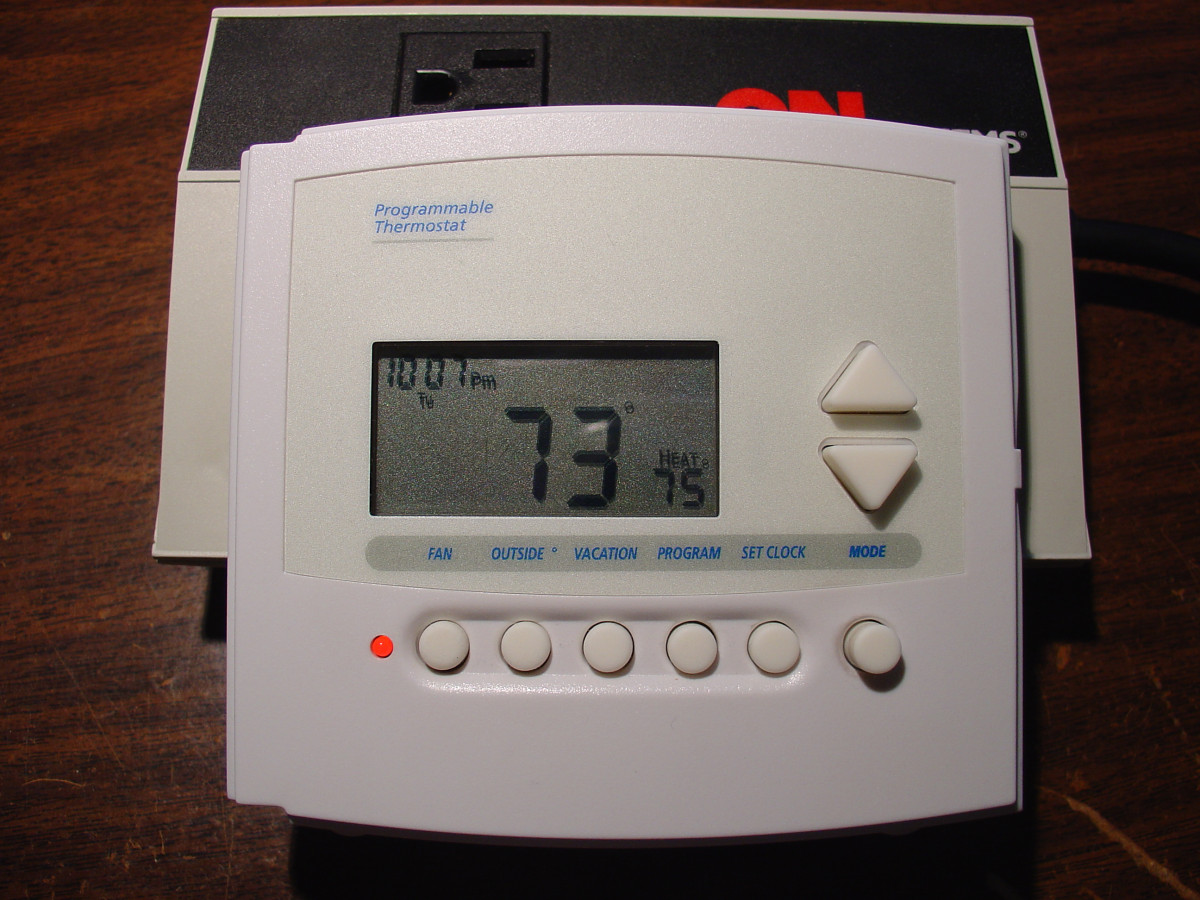
Electronic thermostats: for more autonomy!
On the most recent and advanced radiators, the electric radiator thermostat is electronic and equipped with a temperature sensor:
– This electric radiator programmer can propose up to 6 heating commands: comfort, comfort -1°C, comfort – 2°C, eco, frost protection, and off.
– The temperature sensor modulates the heating according to the temperature variations in the room to maintain the room temperature constant and precise (for some, to the nearest 1/10th of a degree).
– The heating is therefore regulated (automatic switch-off and switch-on) according to the set values displayed.
Centralized electric heating programmers: the most efficient
Much more advanced, the centralized electric heater programmer is coupled with a room thermostat and allows to set a set temperature for the whole house (18°C, for example).
Installation of the electric heater programmer
This type of electric heating controller controls and modulates the operation of each radiator to maintain a constant temperature. It is installed in a reference room (living room, corridor) where the temperature is the most homogeneous. It can thus measure and correct the temperature variations in the house.
Several electric heating controllers can be installed: this allows to divide the house into heating zones and assign an adapted heating mode (temperature, operating ranges) to each one. The radiators associated with the same programmer are therefore managed centrally:
– Wired: the radiators are connected.
– Wireless: the transmission is done by radio waves or infrared.
Programming
The programming can be done according to:
– the time of day: from 8 to 10 am, for example;
– the time of day: day/night, morning/afternoon/evening;
– the day of the week: working days, weekends, Wednesday afternoon for children.
A gadget that quickly pays for itself!
The centralized electric heating programmer has several advantages:
– Energy savings: the energy consumption is necessarily reduced since the electric radiators heat only during the defined time slots.
– Increased comfort: you can anticipate and switch on the bathroom heating 1/4 hour before you wake up or the living room radiator 30 minutes before you return home.
– Ease of use: once the device is set up, you don’t have to worry about it anymore.
The purchase price of a centralized programmer is about $80 for the first models. Since the promise of a 10% energy saving is easily achieved, the investment is more than worth it.
Outdoor sensor: taking into account climatic variations
The outdoor sensor measures the temperature outside the house.
– Coupled with an electric radiator programmer, it reflects the climatic variations on the power demand of the radiators.
– It allows to keep a constant temperature inside the house and shortens the normal reaction time of the system.
– Price: Starting at $40.
Load shedding: avoid overcharging
The load shedder adapts the power consumed to the subscribed power. You can therefore choose to cut off the power supply to certain electric radiators (considered non-priority) when the electricity demand is too high:
– You avoid having the entire installation break down unexpectedly.
– You do not subscribe to a higher band for occasional overconsumption.
– This equipment directly connects to the circuit breaker and the electrical panel.
Note: any heating system will only be efficient in a properly insulated house.





